Week 7 Syntax
本週主題
- 句法理論與計算表徵
句法 | Syntax
句法對於 NLP/NLU 很重要,因爲它涉及語言在表層的結構運作。
但是 (形式) 句法在近代語言學發展史中佔據了很大(太大!)的一部分
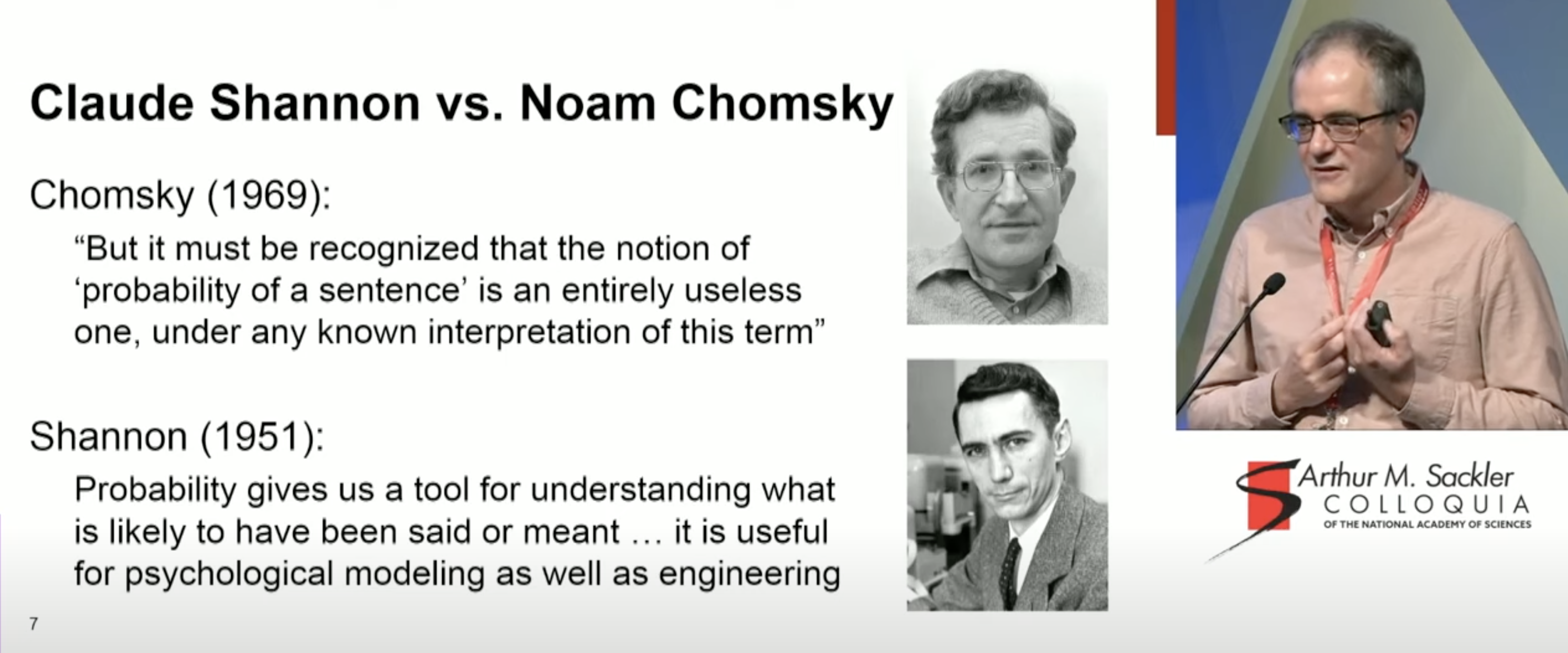
N.Chomsky 對於語料庫,一直到現在的 LLM 的(鄙視)態度都一樣的,爲什麼呢? 2012 on corpus linguistics; 2023 on chatGPT
形式句法
Formal syntax/Geneartive Grammar
Theory
- 【句法】是第一順位。In generative grammar, pride of place is given to syntax, 也具備自己的【獨立模組】。
- 【形式觀】:心智中的句法運算可以完全獨立於意義之外。
Data
- top-down,有限規則駕馭無限表達,重點在掌握 competence 而非 performace。
- 內省式語感判斷 rely on introspective judgments as their primary source of data.
- the poverty-of-stimulus hypothesis (“the child has no data”).
句法的計算表徵
兩種在計算語言學上常使用的句法表徵 (representation):
- dependency
- constituency Defining Constituency
- syntactic constituency is a syntactic unit that is a maximal projection of a syntactic category.
- syntactic category is a set of words that share a common syntactic property.
- N 的 maximal project 是 NP,V 是 VP,PP 是 PP,等等。
從世界語言來看,這個概念是很值得爭議的。
Modeling constituency
目前最爲廣泛用來 model constituency 的形式系統叫做 Context-free Grammar (CfG), 在語言學中稱 Phrase Structure Grammar (PSG) 。
由 Chomsky 在 1950 年代提出,是一種用來描述語言句法結構的形式系統。
Context-free Grammar
a set of rules (or productions) that describe how to construct a sentence from smaller units.
形式上定義,CfG 是一個四元組 (4-tuple) \((N, \Sigma, R, S)\),其中:
- \(N\) 是一個有限集合,稱為 non-terminal symbols,代表句法結構的組成部分。
- \(\Sigma\) 是一個有限集合,稱為 terminal symbols,代表句子中的詞。
- \(R\) 是一個有限集合,稱為 rules,代表句法結構的生成規則。
- \(S\) 是一個 \(N\) 中的元素,稱為 start symbol,代表句子的根節點。
例子
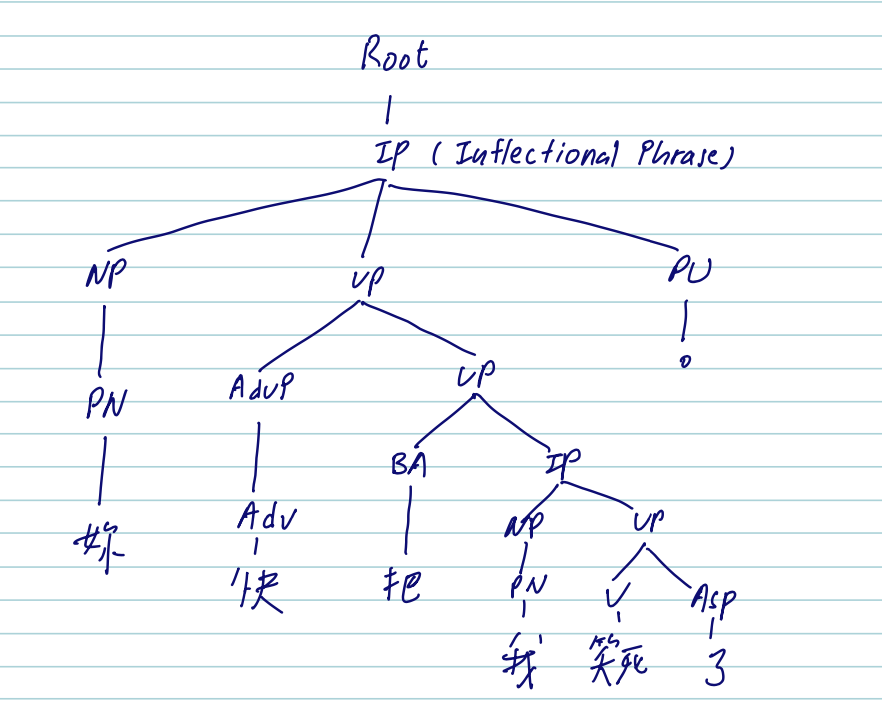
如何解析以下句子?
他說的都不對
處理形式上的各種空缺問題
動詞的論元脫落有不同的符碼標記
- 移位 (那個蘋果,我扔了)
- 隱含(她打算打網球)
- 空格(他買了兩根香蕉,給了他朋友一根)
Parsing
句法剖析
- (自動地) 把一個句子 (a string of word) 映射到其對應的句法結構 (a parse tree),就叫做 parsing。
Treebanks
- 一個 treebank 是一個語料庫,其中的每個句子都有一個對應的句法樹 (parse tree)。
- 這些句法樹通常是由訓練過的語言學家標註、或修訂過的。
例子
Formal language and Chomsky normal form
It is useful to have a normal from (i.e., each of the production/rule taks a particular form) for formal languages, so that we can compare different formal languages and their grammars.
Chomsky normal form (CNF) is a normal form for context-free grammars.
- A grammar is in CNF if all its rules are of the form:
- \(A \rightarrow BC\)
- \(A \rightarrow a\)
- \(S \rightarrow \epsilon\)
- A grammar is in CNF if all its rules are of the form:
- Chomsky-adjunction
Structural Ambiguity
結構歧義
一個句子的句法結構可能有多種不同的解析方式,這就是結構歧義 (structural ambiguity)。
最常見的結構歧義類型:附加 (attachment ambiguity) 和並列 (coordination ambiguity)。
I shot an elephant in my pajamas
練習中文歧義句
\(VP + NP_{1} + de + NP_{2}\)
\(A + NP_{1} + NP_{2}\)
剖析演算法
CKY Parsing algorithms
Dynamic Programming
Evaluation
Defining dependencies
由法國語言學家 Lucien Tesnière 提出。
對於語序較爲自由的、構詞豐富的 (morphologically rich languages) 語言,rule-based approach 很難應付。(以 polymorphic languages 爲例)
此外,找到了主要語 (head) 及其依存 (dependent) 有助於語意剖析 (semantic parsing)。(可以容納句法和語意結構並存)
動詞的配價理論
主要語或中心語
來自化學元素的類比:句子像是分子,由原子組成,而原子的核心是配價 (valence) (按一定的價結合在一起)。
動詞是中心,所有成分都是環繞着中心動詞開展的。
價數、價質(
semantic roles)、價形 (syntactic position)
Dependency 的形式定義
一個句子的 dependency tree 是一個有向無環圖,其中每個節點代表一個詞,每個邊代表一個依存關係 (dependency relation)。
依存關係是一個非對稱的二元關係,其中一個元素是 head,另一個元素是 dependent。
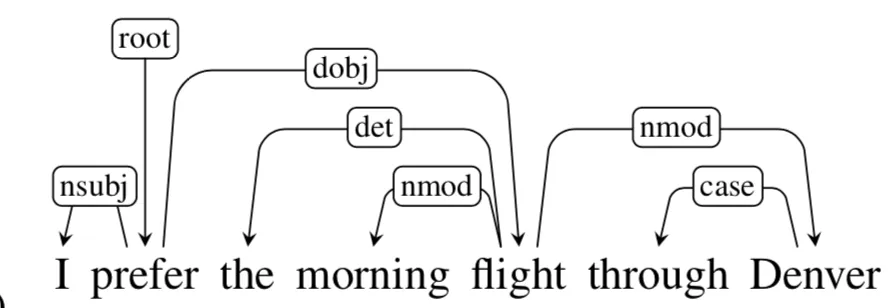
非對稱的關係也帶出了階層的概念,此外,每個元素都可能同時支配與被支配。
幾個概念
Head-Dependent 的箭頭方向:the origin word is the Head and the destination word is Dependent. (e.g., ‘prefer’ is Head & ‘I’ is Dependent.)
Root: Word which is the root of our parse tree. (It is ‘prefer’ in the above example).
Grammar Functions and Arcs: Tags between each Head-Dependent pair is a grammar function determining the relation between the Head & Dependent. The arrowhead carrying the tag is called an Arc.
Dependency relations
- 關係種類有很多分類方式,這裏採取 Universal Dependencies 的分類方式。

Dependency Formalisms
- 圖論上來看,dependencies can be represented as a directed graph \(G= (V, A)\) where V(set of vertices) represents words (and punctuation marks as well) in the sentence & A( set of arcs) represent the grammar relationship between elements of V.
- A dependency parse tree is the directed graph which has the below features:
- Root 沒有傳入的弧 (incoming arc) (can only be Head in Head-Dependent pair)
- 除了 root 之外的每一個節點,應該都只有一條傳入的弧 (Only one Parent/Head)
- 從 root 到每一個節點都只有一條路。
Projectivity
- Projective arc: An
arc/arrows_with_tagare projective when ‘Head’ associated with the arc has a path to reach each word that lies between ‘Head’ & ‘Dependent’.
以 (18.2) 爲例,the 和 flights 的 arc 是 projective,因爲在此的 Head (即 flights) 到它的 Dependent (即 the) 之間有個 morning 這個詞, Head 也有路可到得了。
同樣地,‘canceled’ (HEAD) 到 ‘flights’ (DEPENDENT) 這條 arc 也是 projective,因爲 Head 有路可到達它和其 Dependent 之間的詞。(i.e., ‘the’ (canceled \(\rightarrow\) flights \(\rightarrow\) the) 以及 ‘morning’ (canceled \(\rightarrow\) flights \(\rightarrow\) morning))
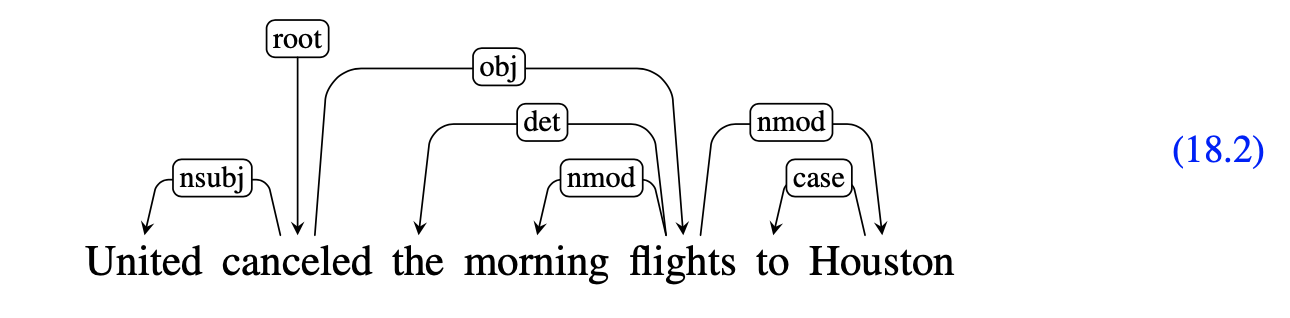
- Projective parse tree: A parse tree with all its arcs projective. The above tree is projective; A tree with at least one of the arcs as non-projective is called non-projective parse tree.
Practice
以下這個 dependency parse tree 是 projective or non-projective? 
Dependency Treebanks
A dependency treebank is a collection of sentences with their corresponding dependency trees.
UD treebanks are available for 100+ languages.
Dependency Parsing
- Transition-based
- Graph-based
後者較準確,處理長句較好,也能生成 non-projective dependency tree (對於不同於英語的其他類型語言很有幫助)。
Graph-based Dependency Parsing
任務的定義:給定一個句子,找出一個 dependency tree,使得它的分數最高。
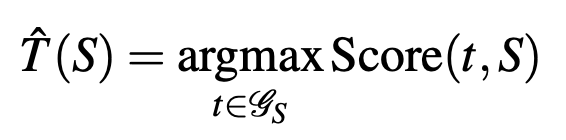
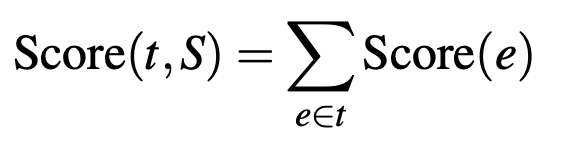
注意:\(y=f(x)\), \(y = maxf(x)\), \(y=argmax f(x)\) 的不同!
Graph-based Dependency Parsing
歸結到兩個問題:
[1] assigning a score to each edge 給邊分數
[2] finding the best parse tree given the scores of all potential edges. 找出最好的依存樹
Chu-Liu/Edmonds’ Algorithm
解 [2] 的方法
It turns out that finding the best dependency parse for \(S\) is equivalent to finding the maximum spanning tree over \(G\).
- Chu-Liu/Edmonds’ Algorithm is a greedy algorithm for finding the maximum spanning tree of a graph.
先要瞭解何謂最大擴張樹 (Maximum Spanning Tree)
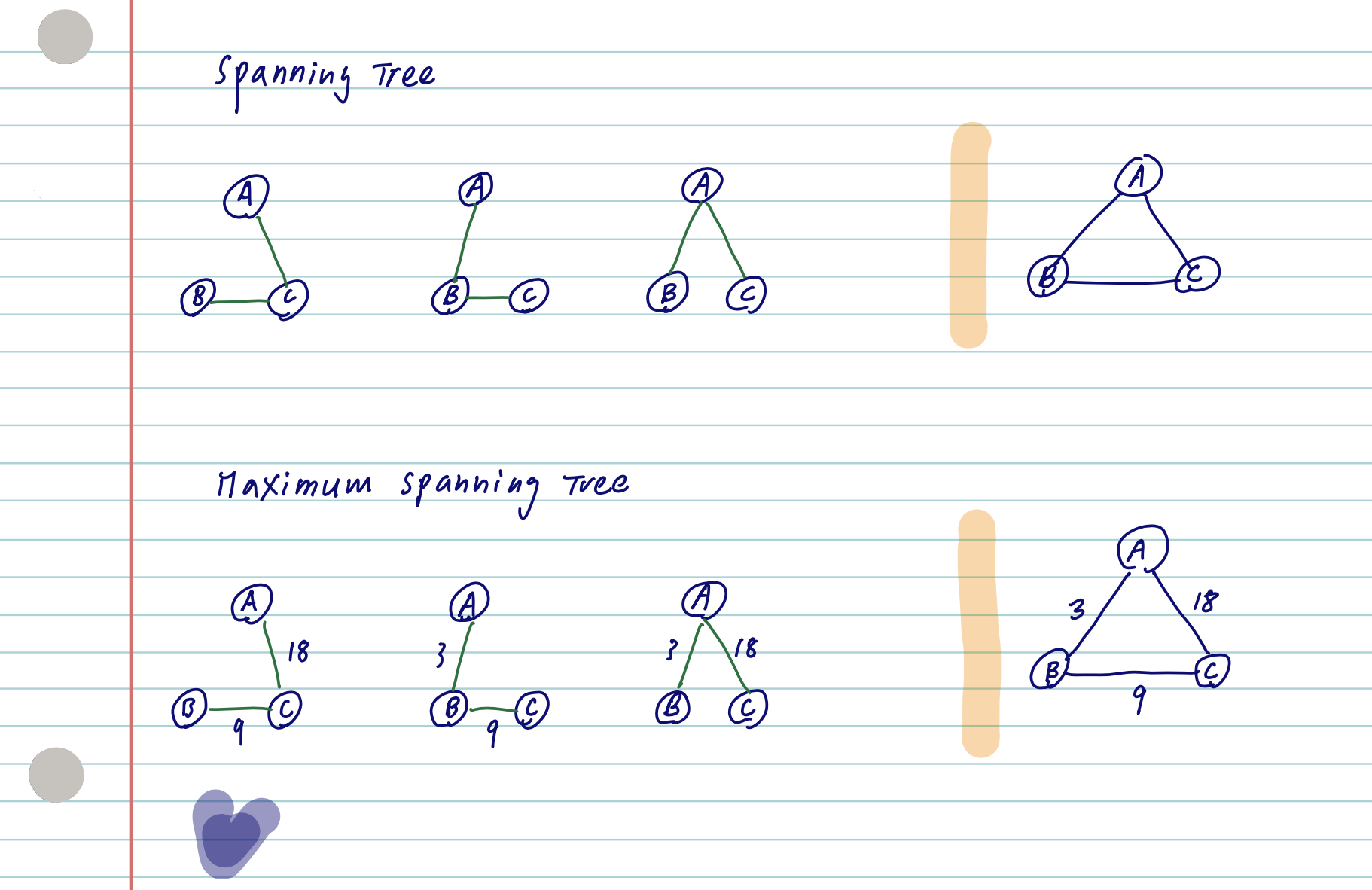
舉例
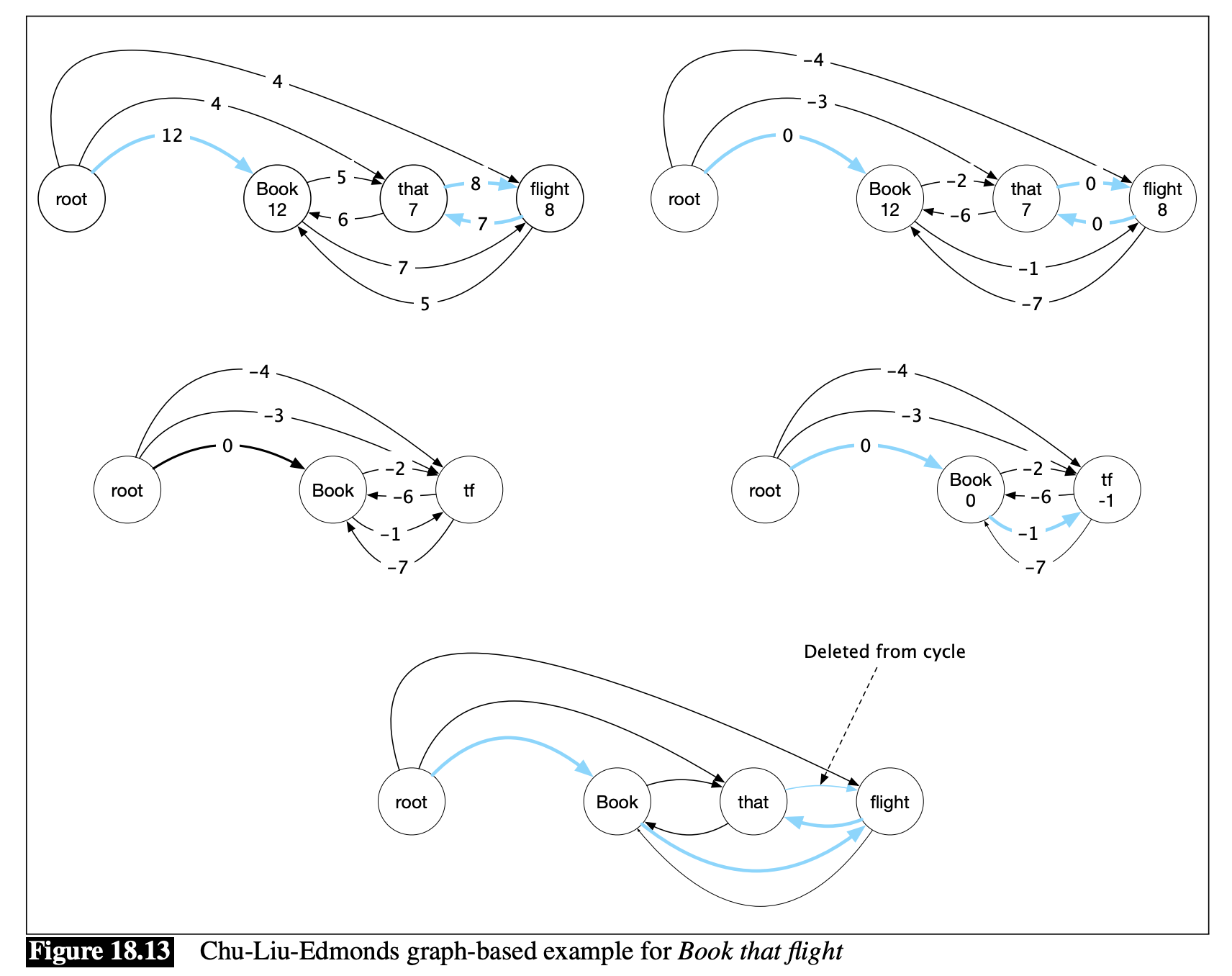
Evaluation
理想上的 exact match 指標是不太可行的。
Labeled Attachment Score (LAS): the ratio of correctly detected Head-Dependent pairs along with their tag / total Head-Dependent pairs in testing data.
Unlabeled Attachment Score (UAS): the ratio of correctly detected Head_Dependent pairs (irrespective of the tag) / total Head-Dependent pairs in testing data.
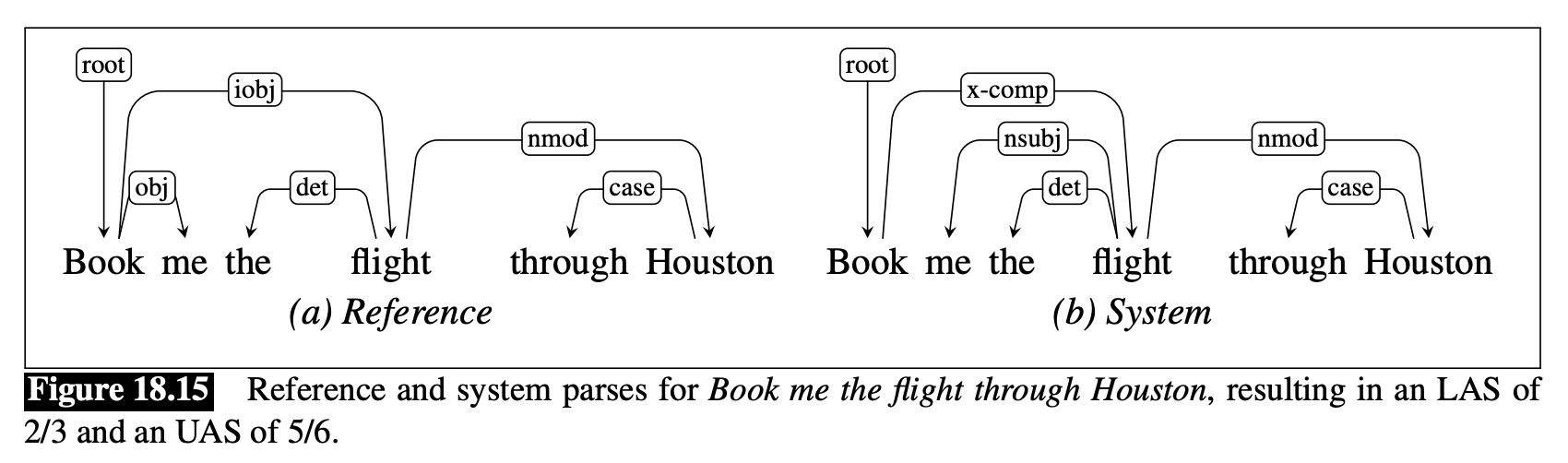
Reference指的是標準答案,System指的是系統生成的答案。Total head-dependent pairs指的是句子中所有的 Head-Dependent pair, 不管在Reference或System都是 6 。Total Head-Dependent pairs correctly detected with tags= 4 (因爲System中的nsubj和det都是正確的)。Total Head-Dependent pairs correctly detected= 5 (因爲只管 pairs,不管 tags,所以 book \(\rightarrow\) flight 也算)。
Dependency Parsing with LLMs
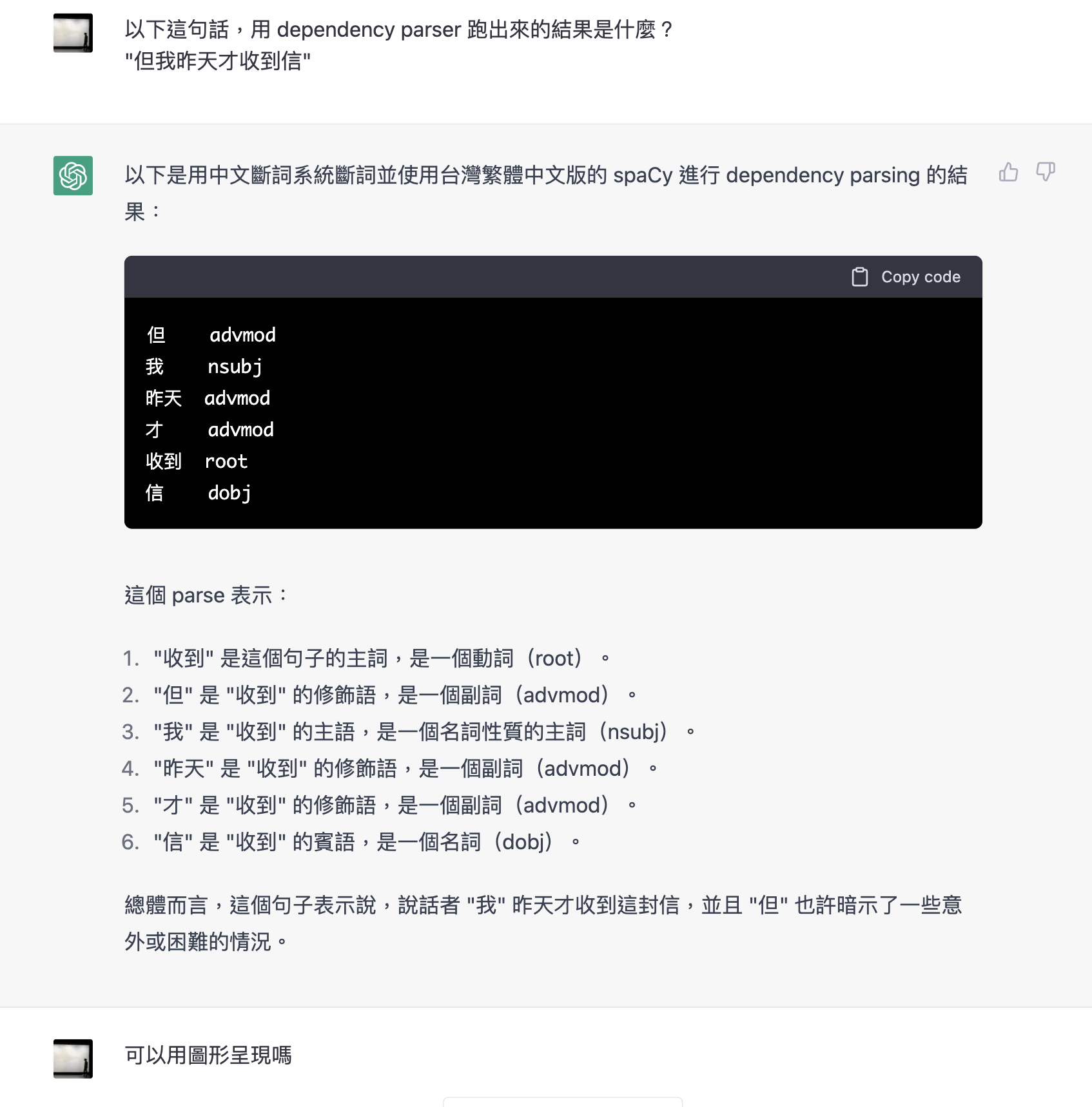
Reflections
- Constituency/Dependency Parsing,強烈預設了動詞爲核心的語言假設,這點需要注意。